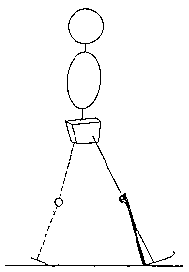
At initial contact, the ground reaction force vector's point of application is ordinarily near the heel.
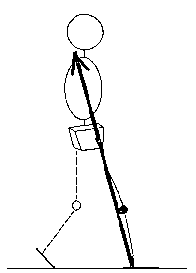
As loading response progresses, the ground reaction force vector moves posterior to the knee, producing a flexor moment.
By contacting the ground initially on a flat foot, the person moves the ground reaction force vector's point of application anteriorly...
so that the more anteriorly situated force vector is closer to the knee joint throughout loading response, and so produces a smaller knee flexor moment during that period.
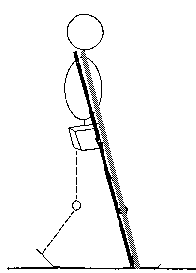
If the ground reaction force moves anterior to the knee joint's lateral axis, it produces a knee extensor moment. Therefore, people may compensate for knee extensor weakness by contacting the floor with a relatively flat foot.

As loading response progresses, the ground reaction force vector moves posterior to the knee, producing a flexor moment.

By contacting the ground initially on a flat foot, the person moves the ground reaction force vector's point of application anteriorly...
so that the more anteriorly situated force vector is closer to the knee joint throughout loading response, and so produces a smaller knee flexor moment during that period.
If the ground reaction force moves anterior to the knee joint's lateral axis, it produces a knee extensor moment. Therefore, people may compensate for knee extensor weakness by contacting the floor with a relatively flat foot.

By contacting the ground initially on a flat foot, the person moves the ground reaction force vector's point of application anteriorly...
so that the more anteriorly situated force vector is closer to the knee joint throughout loading response, and so produces a smaller knee flexor moment during that period.
If the ground reaction force moves anterior to the knee joint's lateral axis, it produces a knee extensor moment. Therefore, people may compensate for knee extensor weakness by contacting the floor with a relatively flat foot.