|
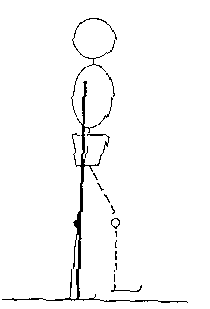
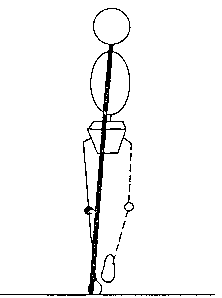
What effect will this have on joint motion and muscle activation?
During midstance, ground reaction forces produce:
- a pronation moment at the subtalar joint
- a varus moment at the knee
- an adduction moment at the hip
The body reponds to these moments with
- activity in the intrinsic foot muscles, soleus, and other
supinator muscles (in order to supinate the subtalar joint make
the foot more rigid to bear the body's full weight).
- passive tension in the lateral knee structures. Active force
in the tensor fascia lata could contribute to knee stability in
the frontal plane
- activity in hip abductor muscles
|
|---|