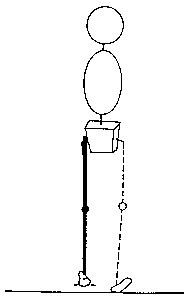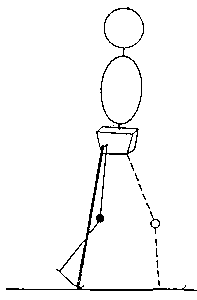
PRESWING (Sagittal plane)
Orientation of ground reaction force vector (GRFV) in sagittal plane
Normal GRF is located
- anterior to ankle joint
- posterior to knee joint
- posterior to hip joint