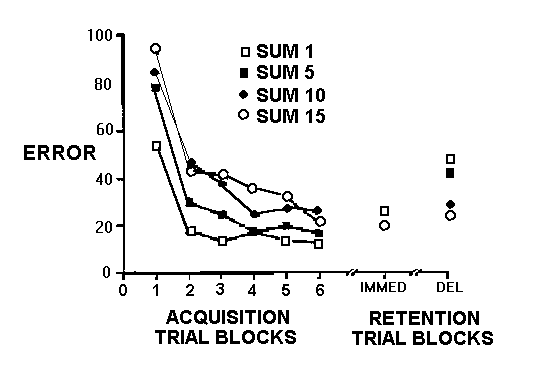

| Summary feedback resulted in poorer short-term acquisition but better retention than continuous (SUM=1) feedback. |
|---|
Schmidt, R.A., Young, D.E., Swinnen, S., & Shapiro, D.C. (1989). Summary knowledge of results for skill acquisition: Support for the guidance hypothesis. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 15, 352-359.
Winstein, C.J. (1991). Knowledge of results and motor learning - implications for physical therapy. Physical Therapy, 71, 140-149.