Each lab group needs:
- Skin pencil (2)
- One copy of each of these texts:
- Kendall, F.P., McCreary, E.K., & Provance, P.G. (1993). Muscles: Testing and Function (4th ed.). Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins.
- Smith, L.K., Weiss, E.L. & Lehmkuhl, L.D. (1996). Brunnstrom's Clinical Kinesiology (5th ed.). Philadelphia: F.A. Davis.
Prepare for lab and lecture by reading pp. 333-342 on the ankle and subtalar joints, and pp. 344-355 on the extrinsic muscles of the foot.
- Anatomy text of your choice
- Palpable structures
Locate on yourself and on a partner the palpable structures listed in your text (Smith, Weiss, & Lehmkuhl, 1996, pp. 333-336).
- medial and lateral malleoli
- sustentaculum tali (on the calcaneus)
- navicular tuberosity
- anterior portion of talus
- deltoid ligament
- first cuneiform
- first metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint line
- calcaneus
- cuboid
- first through fifth metatarsals
- lateral collateral ligaments
- anterior talo-fibular
- posterior talo-fibular
- calcaneo-fibular
-
Extrinsic muscles of the foot
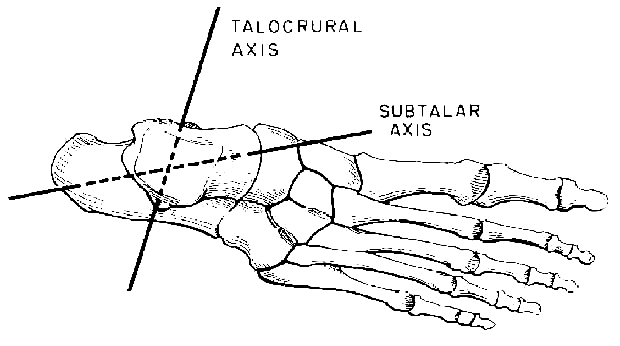
Extrinsic foot muscles are so named because each has an attachment that is located outside the foot. Extrinsic foot muscles are multi-articular; they cross and, therefore, produce movement at more than one articulation or joint. Each extrinsic foot muscle either dorsiflexes or plantar flexes the ankle (talocrural) joint, and either pronates or supinates the subtalar joint.
Use skin pencils to draw lines of application, local to the ankle and subtalar joint, for each extrinsic foot muscle.
Based on the relationship of the relevant line of application, local to the axes of the ankle and subtalar joints (Smith, Weiss, & Lehmkuhl, 1996, Fig. 10-2, p. 337), predict each muscle's action at either joint.
Extrinsic muscles of the foot
Muscle's action at ankle (talocrural) joint
(either DF or PF)
Muscle's action at subtalar joint
either pronation or supination
- tibialis posterior
- flexor digitorum longus
- flexor hallucis longus
- tibialis anterior
- extensor digitorum longus
- extensor hallucis longus
- peroneus longus and brevis
- gastrocnemeus and soleus
- To produce certain movements, extrinsic muscles must act in synergies. List a pair of muscles that, acting in synergy, produce each specific movement.
Ankle dorsiflexion without subtalar pronation or supination
____________________ and _______________________
Ankle plantar flexion without subtalar pronation or supination:
____________________ and ________________________
Subtalar pronation without ankle dorsiflexion or plantar flexion
_____________________ and ________________________
Subtalar supination without ankle dorsiflexion or plantar flexion
_____________________ and ________________________
Last updated 9-19-01 Dave Thompson PT
return to PHTH/OCTH 7143 lab schedule
- Kendall, F.P., McCreary, E.K., & Provance, P.G. (1993). Muscles: Testing and Function (4th ed.). Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins.
- Smith, L.K., Weiss, E.L. & Lehmkuhl, L.D. (1996). Brunnstrom's Clinical Kinesiology (5th ed.). Philadelphia: F.A. Davis.
Prepare for lab and lecture by reading pp. 333-342 on the ankle and subtalar joints, and pp. 344-355 on the extrinsic muscles of the foot. - Anatomy text of your choice
Locate on yourself and on a partner the palpable structures listed in your text (Smith, Weiss, & Lehmkuhl, 1996, pp. 333-336).
- medial and lateral malleoli
- sustentaculum tali (on the calcaneus)
- navicular tuberosity
- anterior portion of talus
- deltoid ligament
- first cuneiform
- first metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint line
- calcaneus
- cuboid
- first through fifth metatarsals
- lateral collateral ligaments
- anterior talo-fibular
- posterior talo-fibular
- calcaneo-fibular
- anterior talo-fibular
- posterior talo-fibular
- calcaneo-fibular
Extrinsic foot muscles are so named because each has an attachment that is located outside the foot. Extrinsic foot muscles are multi-articular; they cross and, therefore, produce movement at more than one articulation or joint. Each extrinsic foot muscle either dorsiflexes or plantar flexes the ankle (talocrural) joint, and either pronates or supinates the subtalar joint.
Use skin pencils to draw lines of application, local to the ankle and subtalar joint, for each extrinsic foot muscle.
Based on the relationship of the relevant line of application, local to the axes of the ankle and subtalar joints (Smith, Weiss, & Lehmkuhl, 1996, Fig. 10-2, p. 337), predict each muscle's action at either joint.

|
|---|
Extrinsic muscles of the foot
Muscle's action at ankle (talocrural) joint
(either DF or PF)
Muscle's action at subtalar joint
either pronation or supination
|
|
| |
|---|
Ankle dorsiflexion without subtalar pronation or supination
____________________ and _______________________
Ankle plantar flexion without subtalar pronation or supination: | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Subtalar pronation without ankle dorsiflexion or plantar flexion
_____________________ and ________________________
Subtalar supination without ankle dorsiflexion or plantar flexion
_____________________ and ________________________ |
return to PHTH/OCTH 7143 lab schedule