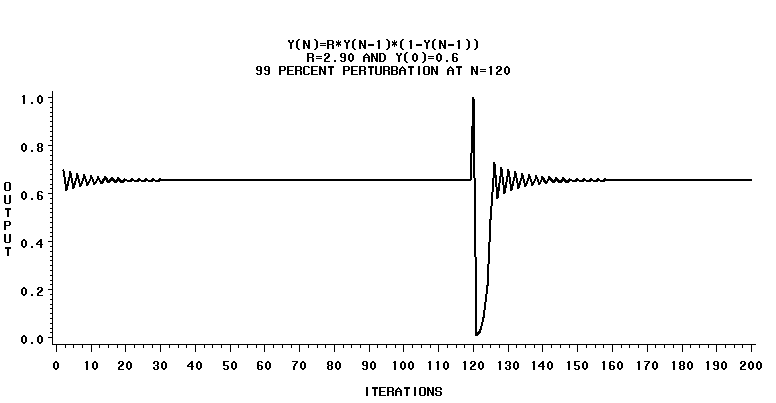
 Proximity to a bifucation is detectable by examining a perturbation's effect on relaxation time.
Proximity to a bifucation is detectable by examining a perturbation's effect on relaxation time.
This equation produces stable behavior, including stable and bistable states. It also produces bifurcations, and periods of chaotic behavior.
 Proximity to a bifucation is detectable by examining a perturbation's effect on relaxation time.
Proximity to a bifucation is detectable by examining a perturbation's effect on relaxation time.
download an Excel file to model the logistic difference equation, inserting different values for the initial conditions (x1) and the "nonlineariry factor" (r).