History: The patient was a 56 year-old man who developed a non-healing raised ulcer on his lower lip about 1.2 cm on surface dimension. Grossly, a firm nodule could be palpated at this location. A small biopsy was taken and reviewed squamous cell carcinoma. The current specimen is the product of a wedge resection of this specimen.
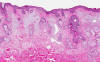
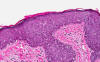
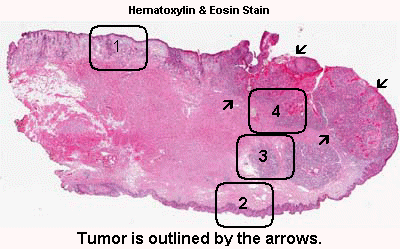
Anatomy: There are structure that indicate that this is a lip. This specimen is in fact taken at the mucoepidermoid junction. While one side is covered by squamous cell epithelium with skin appendages (Area 1), the other side side is covered by squamous cell epithelium alone without skin appendages (Area 2). In addition, there are minor salivary glands (Area 3) near this squamous epithelium. This side is the mucosal side of the lip.
Histologic Highlights of this Case:
-
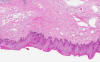
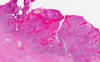
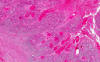
The tumor is delimited by the arrow as you can see here. At scanning-magnification, the mass appears as an area that disrupts the normal anatomy. Some fresh blood is present and most likely due to bleeding secondary to the ulcerated tumor.
-
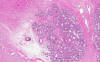
In deeper part of the tumor, numerous finger like invading tumors are extending into the stromal tissue and is accompanied by a substantial amount of reactive lymphocytes (Area 4).
-
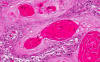
On high magnifiation, keratin pearls are present which indicate that this is a keratinizing tumor. Compare the size of the nuclei of the carcinoma cells with that of the adjacent nuclei in the normal mucosa. They are much larger.