|
History: The patient was a 75 year-old man who presented with a
pedunculated, submucosal tumor at the base of the tongue as illustrated
in the CT scan. A fine needle aspiration was performed and
an excision was subsequently performed. The excised specimen was a 6.0 x
3.5 x 2.0 cm mass with solid cut surface that was free of cystic changes
or necrosis.
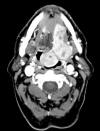
CT Scan
Histologic Highlights of this Case:
-
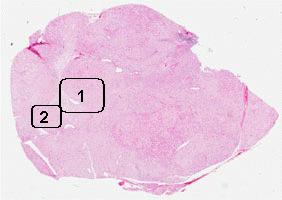
Histologically, the tumor is a well
circumscribed neoplasm with pushing margin. The tumor cells are
large and polygonal with one or two small, bland, and eccentrically
placed nuclei. While a significiant number of the tumor cells have a
fine granular, amphophilic to eosinophilic cytoplasm , many tumor
cells are dominated by a large centrally located vacule that pus the
cytoplasm to the periphery to become a rim (Area 1). In some cells,
bright eosinophilic rods can be seen (Area 2) and these material
represents Z-band material. Prominent nucleoli are noted in some of
the tumor cells. Mitoses are not readily seen and there is no
hemorrhage or necrosis.
-
Some of the vacuolated cells has a
central mass of stellate cytoplsm with thin strands connected to a
condensed rim of cytoplasm at the periphery (spider cells).
-
The tumor cells are separated by thin
fibrous septa and narrow vascular challesls.
-
Results of immunohistochemistry and
special stain are as follow:
Immunohistochemistry:
·
Muscle
specific actin and smooth muscle actin: Positive in tumor cells.
·
Desmin
and myogenin: Negative in tumor cells.
·
Vimentin:
Negative in tumor cells.
·
CD163:
Negative in tumor cells.
·
PGP9.5:
Negative in tumor cells.
·
S100
protein: Negative in tumor cells.
·
Cytokeratins : Negative in tumor cells
·
Epithelial membrane antigen: Negative in tumor cells.
Special stain:
·
Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS): Negative in tumor cells
·
PAS with diastase: Negative in tumor cells
Comment:
-
Striations can be seen in most case but
does not seem to be a prominent structure in this case.
-
The major differential diagnosis of this
case is granular cell tumor. Tongue is a common location for
granular cell tumor. Although granular cell tumors also have fine,
granular cytoplasm and large polygonal cells with small nuclei, they
do not have the large cytoplasmic vacuoles. Granular cell tumors are
strongly positive for PAS stain. Also, granular cell tumors are
strongly positive for S100 protein. Also, since granular cell tumor
has substantial amount of lysosomes, these tumors are also positive
for CD163. Immunohisochemically, adult rhabdomyoma are positive for
muscle-specific actin and desmin and less commonly for vimentin,
S-100 protein, and Leu-7. The other less common entities for
differential diagnosis include hibernoma (with numerous small
cytoplasmic vacuoles), crystal-storing histiocytosis associated with
lymphoplasmacytic neoplasm (crystal storing cells and histiocytes
are positive for PAS and CD68 but negative for skeletal muscle
markers and S-100 protein), paraganglioma, and cardiac rhabdomyoma.
|