Online Slide/Full Screen/Open with ImageScope
Case No.: N-028
Diagnosis: Sepsis associated with Candida albicans, post mortem growth of Candida albicans, neuronal necrosis in pons, blood in ventricle secondary to germinal matrix hemorrhage
Organ: Pons, Brain
Last Updated: 12/21/2011
|
|
 Online Slide/Full Screen/Open with ImageScope |
|
Hematoxylin & eosin |
Area 1: Necrotic neurons in premature infants typical present as apoptotic cells (black arrow). Note that scant candida fungal hyphae are present (white arrow) |
|
Hematoxylin & eosin |
Area 2: In other areas, there is intense perivascular inflammatory cell infiltration. A few fungal hyphae are noted on hematoxylin and eosin stain (arrow). |
|
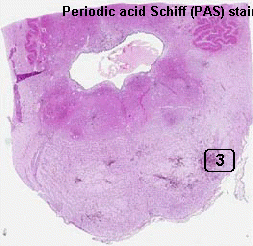
PAS Stain |
Area 3: Numerous hyphae are demonstrated by PAS stain. |
|
History: The deceased baby was born at 29 weeks of gestation and survived for 14 days before death. The mother had premature rupture of membrane and was treated with antibiotic. The baby suffered respiratory distress immediately after birth and was admitted to the intensive care unit. The baby subsequently developed sepsis associated with positive culture for E. coli and expired.
General Autopsy: There were multifocal necrosis involving the heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, spleen, pancreas, thymus, and transmural necrosis of small and large intestines diagnostic of necrotizing enterocolitis. There was also severe hemorrhagic necrotizing pneumonia. Post mortem culture demonstrated Candida albicans.
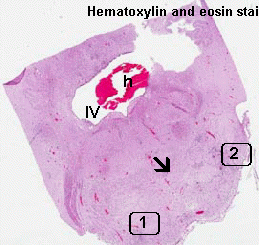
Gross Neuropathologic Findings: The brain weight was within normal limits for the claimed gestational age and there was no evidence of malformation. There is hemorrhage near the ventricular surface of the basal ganglia and the hemorrhage extends into bilateral ventricles with formation of a blodd cast.
Histologic Highlights of this Case: HE stain PAS stain
Comment:
|
Bonus Images:
|
Hematoxylin & eosin |
High magnification of apoptotic cells: This image is taken from another case that is taken at high magnification to reveal the details of apoptotic cells (arrow). This image is also taken from the pons. |
Original slide is contributed by Dr. Kar-Ming Fung, University of Oklahoma Health Science Center, Oklahoma, U.S.A.