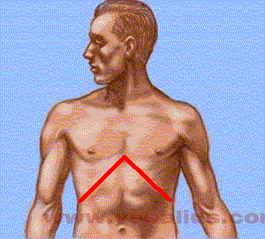
While the rectus abdominus is active for both of these trunk flexion tasks, one or the other of the abdominal oblique muscles predominates, depending on the task. You can determine which of the abdominal obliques is more active by observing the person's infrasternal angle (the angle formed by the anterior costal margins).
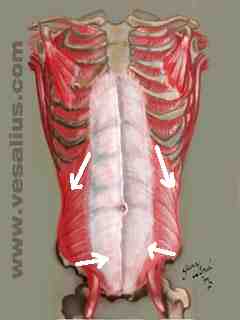
Detailed diagrams of these fan-shaped muscles, their lines of application, and their attachments to the ribcage are available in Kendall, McCreary, & Provance (1993, p.150).
The angle increases or widens when the internal obliques, acting bilaterally, are more active than the external obliques.
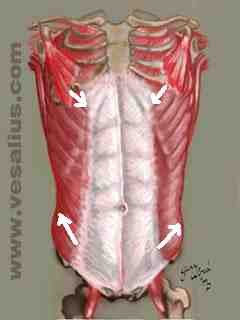
The angle decreases or narrows when the external oblique's activity predominates.


Detailed diagrams of these fan-shaped muscles, their lines of application, and their attachments to the ribcage are available in Kendall, McCreary, & Provance (1993, p.150).
The angle increases or widens when the internal obliques, acting bilaterally, are more active than the external obliques.
