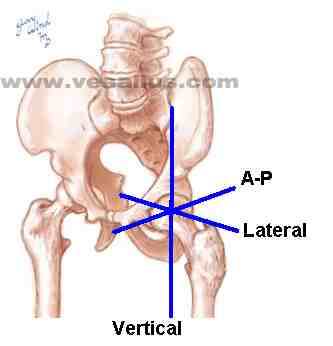
lateral axis: projects to body's surface near greater trochanter
A-P axis: at groin, midpoint of inguinal line
vertical (mechanical) axis of hip: a line that connects femur's points of contact with acetabulum and tibia (Kendall, McCreary, & Provance, 1993, p.230).